Doubly Linked List: list<T>
list00: data structure
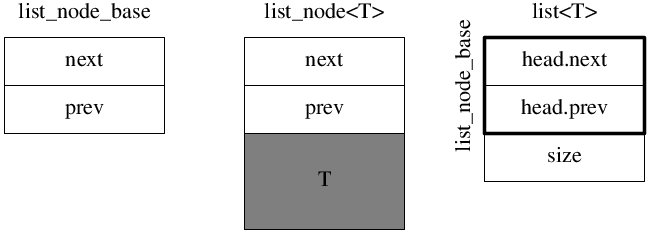
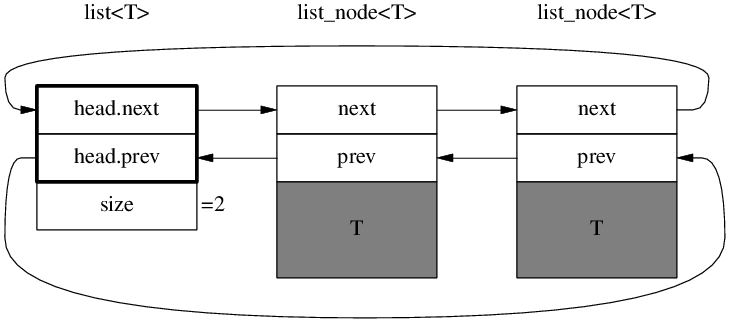
Doubly linked list:
list00.cc:
namespace leanstl
{
struct list_node_base
{
list_node_base* next;
list_node_base* prev;
};
template <typename T>
class list
{
public:
list()
{
head_.next = &head_;
head_.prev = &head_;
}
private:
struct list_node : list_node_base
{
T value_;
};
list_node_base head_;
size_t size_ = 0;
};
} // namespace leanstl
Object sizes on 64-bit Linux.
sizeof void*: 8
sizeof size_t: 8
sizeof list_node_base: 16
sizeof list: 24
T = int
sizeof T: 4
sizeof list_node: 24
T = std::string
sizeof T: 8
sizeof list_node: 24
T = std::vector<int>
sizeof T: 24
sizeof list_node: 40
Object sizes on 32-bit Linux.
sizeof void*: 4
sizeof size_t: 4
sizeof list_node_base: 8
sizeof list: 12
T = int
sizeof T: 4
sizeof list_node: 12
T = std::string
sizeof T: 4
sizeof list_node: 12
T = std::vector<int>
sizeof T: 12
sizeof list_node: 20
list01: destructor
template <typename T>
class list
{
public:
list()
{
head_.next = &head_;
head_.prev = &head_;
}
~list()
{
for (list_node_base* n = head_.next; n != &head_;)
{
list_node* tod = static_cast<list_node*>(n);
n = n->next;
delete tod;
}
}
list(const list& rhs) = delete;
void operator=(const list& rhs) = delete;
// Tentative, so that we can test non-empty lists
void push_front(T x)
{
list_node* n = new list_node(std::move(x));
n->next = head_.next;
n->next->prev = n;
head_.next = n;
n->prev = &head_;
size_++;
}
T& front()
{
return static_cast<list_node*>(head_.next)->value_;
}
private:
struct list_node : list_node_base
{
T value_;
list_node(T&& x) : value_(std::move(x)) {}
};
list_node_base head_;
size_t size_ = 0;
};
Mistake: use-after-free
list01err0.cc
~list()
{
// WRONG: use-after-free
for (list_node_base* n = head_.next; n != &head_; n = n->next)
{
delete static_cast<list_node*>(n);
}
}
int main()
{
leanstl::list<int> li;
li.push_front(43);
printf("front=%d\n", li.front());
}
$ code/bin/list01err0
front=43
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
$ gdb code/bin/list01err0 core
Core was generated by `code/bin/list01err0'.
Program terminated with signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
#0 0x0000000000400847 in leanstl::list<int>::~list (this=0x7ffd3dff5da0) at list01err0.cc:30
30 for (list_node_base* n = head_.next; n != &head_; n = n->next)
(gdb) p n
$1 = (leanstl::list_node_base *) 0x0
(gdb) p *this
$2 = {
head_ = {
next = 0x181e010,
prev = 0x181e010
},
size_ = 1
}
(gdb) p *head_.next
$3 = {
next = 0x0,
prev = 0x7ffd3dff5da0
}
Some clever person finds a way to avoid coredump, by deleting from tail to head.
list01err0hack.cc
~list()
{
// STILL WRONG: use-after-free
for (list_node_base* n = head_.prev; n != &head_; n = n->prev)
{
delete static_cast<list_node*>(n);
}
}
Valgrind
==56399== Invalid read of size 8
==56399== at 0x400847: leanstl::list<int>::~list() (list01err0.cc:30)
==56399== by 0x4007C6: main (list01err0.cc:75)
==56399== Address 0x5a02040 is 0 bytes inside a block of size 24 free'd
==56399== at 0x4C2A360: operator delete(void*) (vg_replace_malloc.c:507)
==56399== by 0x400842: leanstl::list<int>::~list() (list01err0.cc:32)
==56399== by 0x4007C6: main (list01err0.cc:75)
Address sanitizer
$ bin/list01err0asan
front=43
=================================================================
==57074==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-use-after-free on address 0x60300000efe0 at pc 0x400de5 bp 0x7ffe324e9ee0 sp 0x7ffe324e9ed8
READ of size 8 at 0x60300000efe0 thread T0
#0 0x400de4 in leanstl::list<int>::~list() code/list01err0.cc:30
#1 0x400c3f in main code/list01err0.cc:73
#2 0x7f19eb9f7b44 in __libc_start_main (/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6+0x21b44)
#3 0x400a78 (code/bin/list01err0asan+0x400a78)
0x60300000efe0 is located 0 bytes inside of 24-byte region [0x60300000efe0,0x60300000eff8)
freed by thread T0 here:
#0 0x7f19ec5f8477 in operator delete(void*) (/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libasan.so.1+0x55477)
#1 0x400dc3 in leanstl::list<int>::~list() code/list01err0.cc:32
#2 0x400c3f in main code/list01err0.cc:73
#3 0x7f19eb9f7b44 in __libc_start_main (/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6+0x21b44)
previously allocated by thread T0 here:
#0 0x7f19ec5f7fff in operator new(unsigned long) (/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libasan.so.1+0x54fff)
#1 0x400e34 in leanstl::list<int>::push_front(int) code/list01err0.cc:41
#2 0x400bda in main code/list01err0.cc:72
#3 0x7f19eb9f7b44 in __libc_start_main (/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6+0x21b44)
SUMMARY: AddressSanitizer: heap-use-after-free code/list01err0.cc:30 leanstl::list<int>::~list()
Mistake: delete pointer of list_node_base*
list01err1.cc
~list()
{
// WRONG: delete base pointer without virtual dtor
for (list_node_base* n = head_.next; n != &head_;)
{
list_node_base* tod = n;
n = n->next;
delete tod;
}
}
TODO: quote standard on this undefined behavior.
Valgrind
==56456== HEAP SUMMARY:
==56456== in use at exit: 30 bytes in 1 blocks
==56456== total heap usage: 4 allocs, 3 frees, 102 bytes allocated
==56456==
==56456== LEAK SUMMARY:
==56456== definitely lost: 30 bytes in 1 blocks
Address sanitizer (clang 3.9.0)
==57346==ERROR: LeakSanitizer: detected memory leaks
Direct leak of 30 byte(s) in 1 object(s) allocated from:
#0 0x4e7e7b (code/bin/list01err1asan+0x4e7e7b)
#1 0x7fa4984c1e98 (/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6+0xbee98)
SUMMARY: AddressSanitizer: 30 byte(s) leaked in 1 allocation(s).
Double mistake:
~list()
{
// DOUBLY WRONG
for (list_node_base* n = head_.next; n != &head_; n = n->next)
{
delete n;
}
}
Execrise: try memory checker with this double error.
list01alt: list_node_base with protected destructor
struct list_node_base
{
list_node_base* next;
list_node_base* prev;
// prevent deleting a pointer of list_node_base* which actually points to a list_node<T>
// GCC had bug https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=54812 on this, fixed in 4.9.0
protected:
~list_node_base() = default;
};
template <typename T>
struct list_node : list_node_base
{
T value_;
list_node(T&& x) : value_(std::move(x)) {}
};
template <typename T>
class list
{
public:
list()
: head_(0)
{
head_.next = &head_;
head_.prev = &head_;
}
private:
list_node<size_t> head_; // size is head_.value_
};
TODO: Why not virtual dtor?
Site note: GCC Bug 54812
struct Base
{
private:
~Base() = default;
};
int main()
{
Base* p = new Base;
delete p;
}
list02: iterator
list02.cc:
template <typename T>
class list
{
public:
class iterator
{
public:
iterator(list_node_base* n = nullptr) : node_(n) {}
T& operator*() { return *operator->(); }
T* operator->() { return &static_cast<list_node*>(node_)->value_; }
iterator& operator++() { node_ = node_->next; return *this; }
iterator operator++(int) { iterator old = *this; operator++(); return old; }
iterator& operator--() { node_ = node_->prev; return *this; }
iterator operator--(int) { iterator old = *this; operator--(); return old; }
bool operator==(iterator rhs) const { return node_ == rhs.node_; }
bool operator!=(iterator rhs) const { return node_ != rhs.node_; }
private:
list_node_base* node_;
};
iterator begin() { return iterator(head_.next); }
iterator end() { return iterator(&head_); }
};
list02const: const_iterator
list02const.cc:
class const_iterator
{
public:
const_iterator(const list_node_base* n = nullptr) : node_(n) {}
const T& operator*() { return *operator->(); }
const T* operator->() { return &static_cast<const list_node*>(node_)->value_; }
const_iterator& operator++() { node_ = node_->next; return *this; }
const_iterator operator++(int) { const_iterator old = *this; operator++(); return old; }
const_iterator& operator--() { node_ = node_->prev; return *this; }
const_iterator operator--(int) { const_iterator old = *this; operator--(); return old; }
bool operator==(const_iterator rhs) const { return node_ == rhs.node_; }
bool operator!=(const_iterator rhs) const { return node_ != rhs.node_; }
private:
const list_node_base* node_;
};
CRTP ?
list03: copy control
list03.cc:
template <typename T>
class list
{
public:
list()
{
init_head();
}
list(const list& rhs) : list()
{
for (const T& x: rhs)
{
push_back(x);
}
}
list(list&& rhs) : list() { take_over(rhs); }
// Effective Modern C++, Item 41.
list& operator=(list rhs) { swap(rhs); return *this; }
void swap(list& rhs)
{
list tmp(std::move(rhs));
rhs.take_over(*this);
take_over(tmp);
}
void push_front(T x)
{
list_node* n = new list_node(std::move(x));
insert_node(head_.next, n);
size_++;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
list_node* n = new list_node(x);
insert_node(&head_, n);
size_++;
}
private:
struct list_node : list_node_base
{
T value_;
list_node(const T& x) : value_(x) {}
list_node(T&& x) : value_(std::move(x)) {}
};
void insert_node(list_node_base* pos, list_node* n)
{
n->next = pos;
n->prev = pos->prev;
pos->prev->next = n;
pos->prev = n;
}
void init_head()
{
head_.next = &head_;
head_.prev = &head_;
}
void take_over(list& rhs)
{
assert(size_ == 0);
assert(head_.next == &head_);
assert(head_.prev == &head_);
if (rhs.size_ > 0)
{
head_.next = rhs.head_.next;
head_.prev = rhs.head_.prev;
head_.next->prev = &head_;
head_.prev->next = &head_;
rhs.init_head();
size_ = rhs.size_;
rhs.size_ = 0;
}
}
list_node_base head_;
size_t size_ = 0;
};
Mistake
list(const list& rhs) // WRONG: head_ is uninitialized
{
for (const T& x: rhs)
{
push_back(x);
}
}
TODO: memory sanitizer and Valgrind
Composition vs. inheriance
class list_base
{
protected:
list_base()
{
init_head();
}
~list_base()
{
if (size_ == 0)
{
assert(head_.next == &head_);
assert(head_.prev == &head_);
}
}
void init_head()
{
head_.next = &head_;
head_.prev = &head_;
}
list_node_base head_;
size_t size_ = 0;
};
template <typename T>
class list : private list_base
{
public:
list() {}
list(const list& rhs)
{
for (const T& x: rhs)
{
push_back(x);
}
}
list(list&& rhs) { take_over(rhs); }
list04: more constructors
explicit list(size_t n)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
insert_node(&head_, new list_node);
size_ = n;
}
list(size_t n, const T& value)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
push_back(value);
}
struct list_node : list_node_base
{
T value_;
list_node() : value_() {}
list_node(const T& x) : value_(x) {}
list_node(T&& x) : value_(std::move(x)) {}
};
Mistake
struct list_node : list_node_base
{
T value_;
list_node() {} // WRONG: value_ is unitialized for primitive types
list_node(const T& x) : value_(x) {}
list_node(T&& x) : value_(std::move(x)) {}
};
TODO: Valgrind
But memory sanitizer doesn't catch this.
InputIterator vs. Integer
list(const list& rhs) : list(rhs.begin(), rhs.end()) {}
template <typename InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
initialize(first, last, typename std::is_integral<InputIterator>::type());
}
list(std::initializer_list<T> il) : list(il.begin(), il.end()) {}
template <typename InputIterator>
void initialize(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, std::false_type)
{
for (; first != last; ++first)
push_back(*first);
}
template <typename Integer>
void initialize(Integer n, Integer value, std::true_type)
{
for (Integer i = 0; i < n; ++i)
push_back(value);
}